Treatment with the help of the patient’s own information
in the BICOM® mobile VET bioresonance device
In contrast to other “frequency therapy devices”, BICOM® bioresonance is a method that is highly individual and perfectly tailored to the needs of the patient through the use of the patient’s own information and the possibility of testing specific wave patterns for resonance.
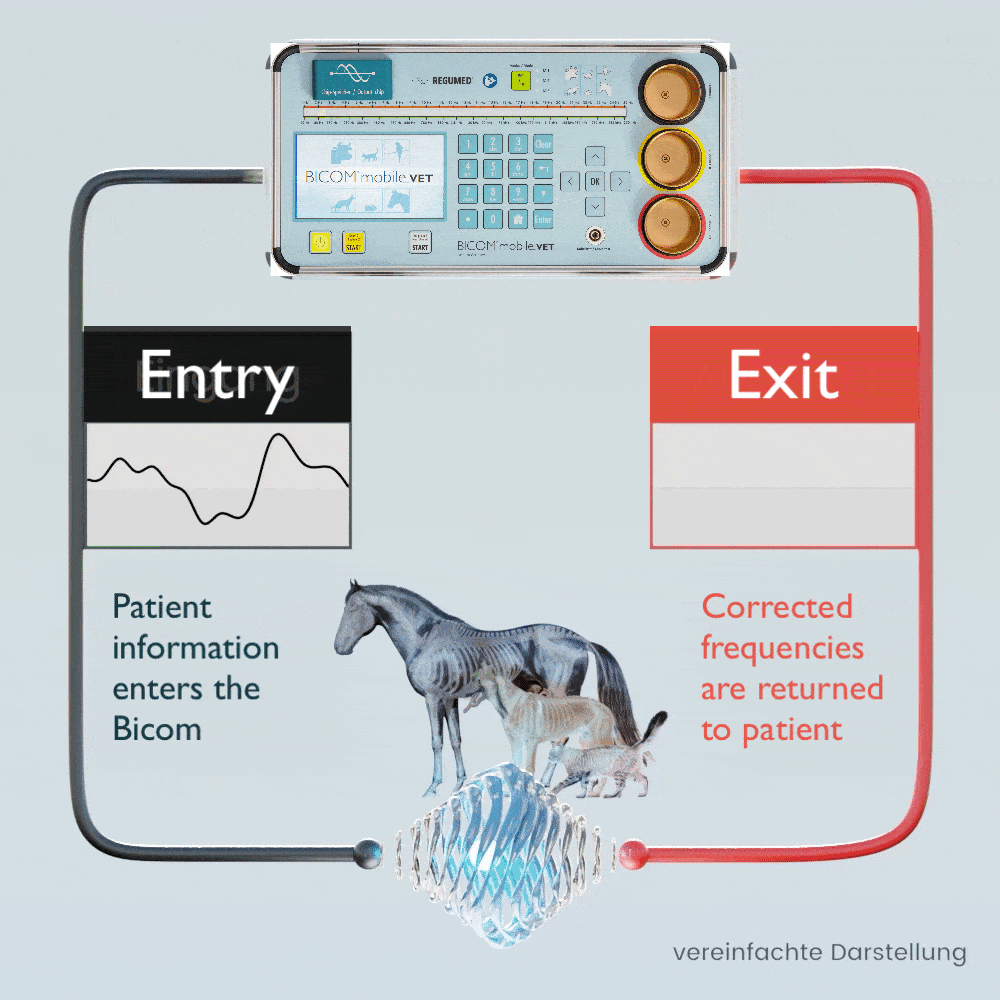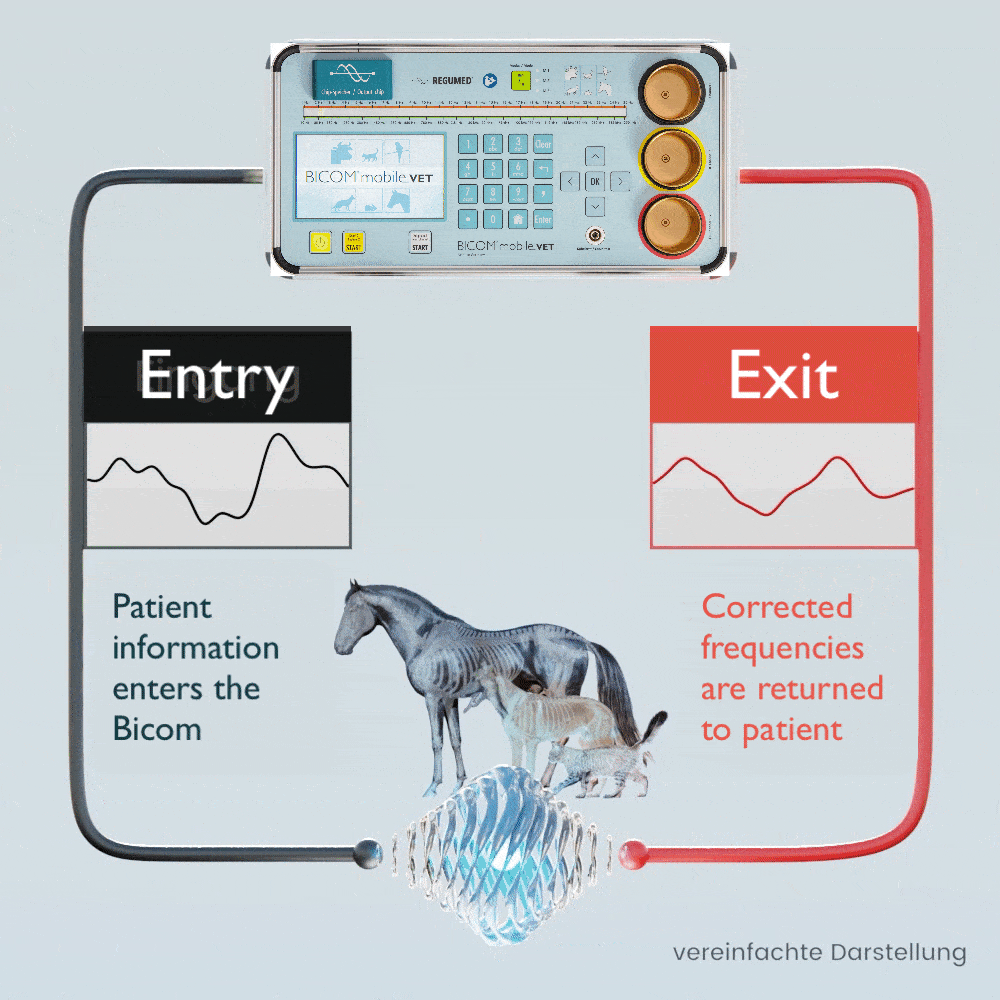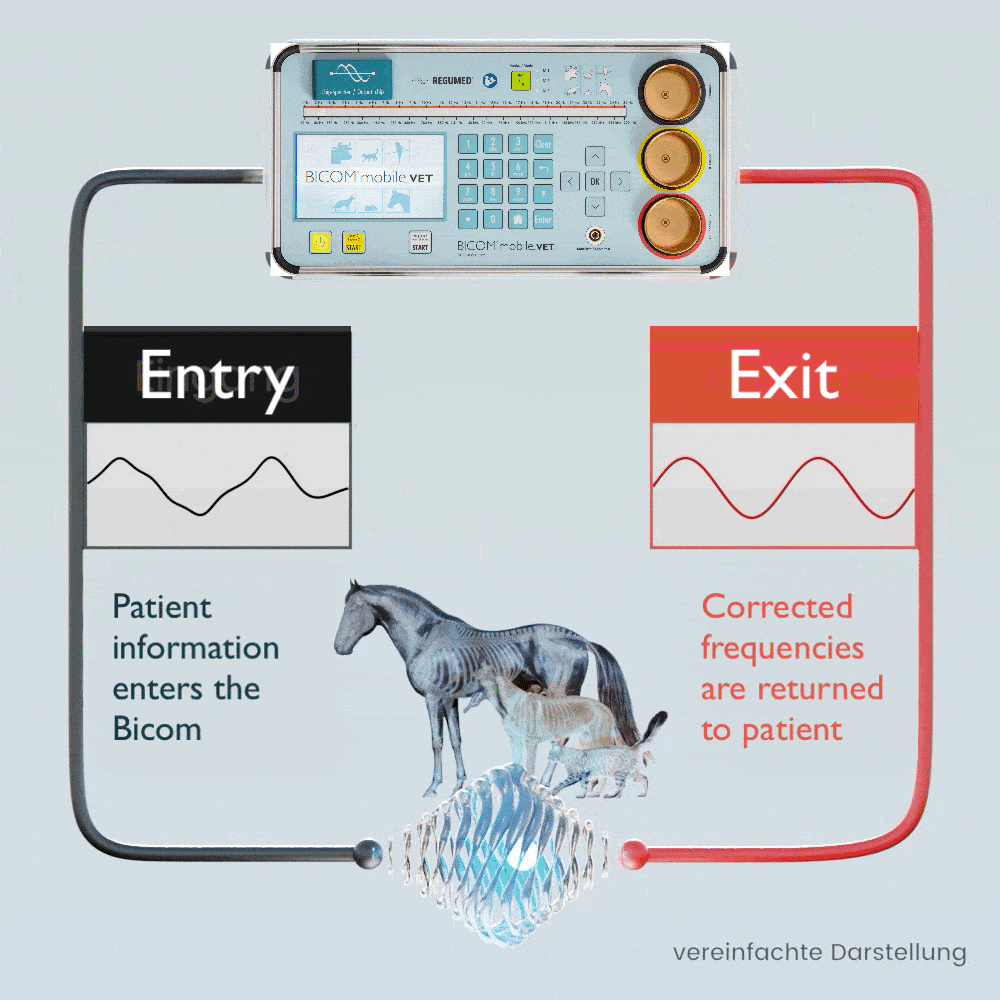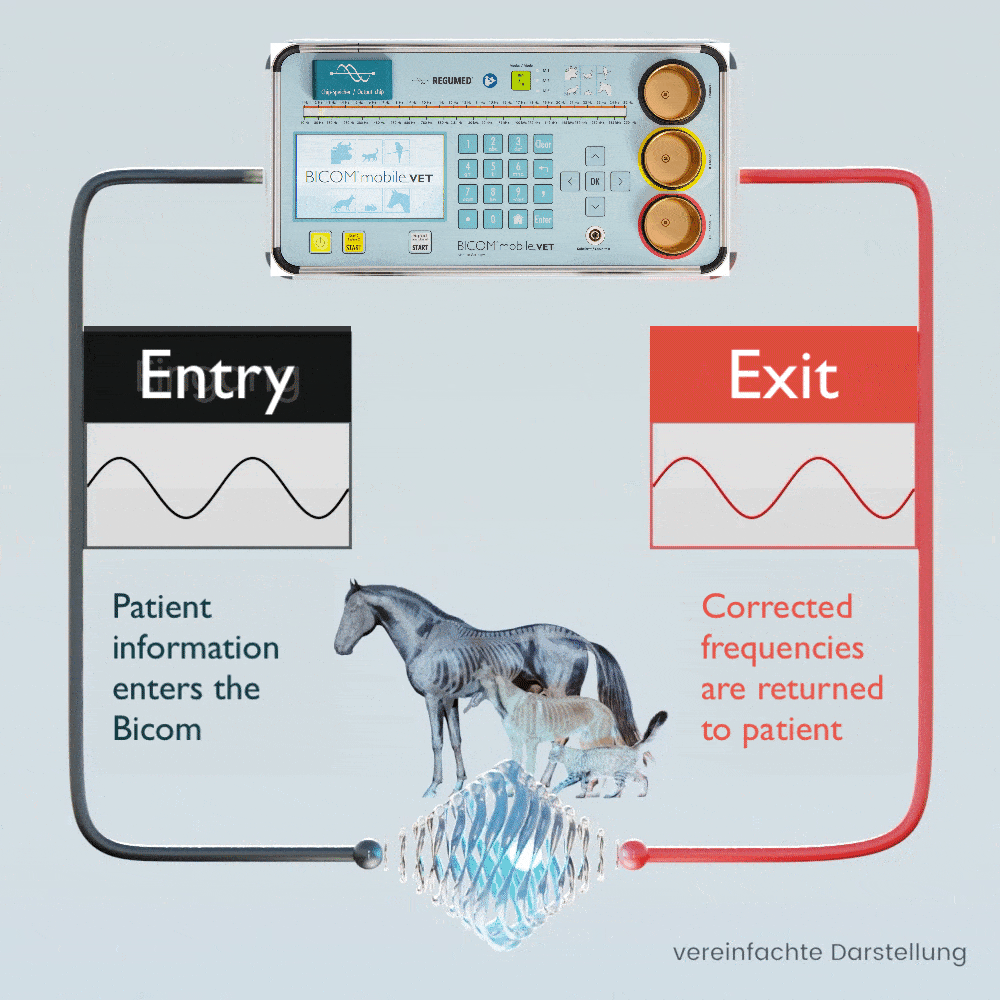
The patient’s own pathological and physiological information is recorded using special applicators and fed into the BICOM® mobile VET.
Depending on the therapy program, the specific wave pattern as a carrier of information is amplified, weakened or inverted and transmitted back to the patient in modulated form, which means that the transmission of information changes in clarity depending on the modulation or it disappears completely.
The treatment signals continuously adapt to the changing pathological situation of the patient. As the therapy progresses, the body’s ability to regulate is reactivated.
Find out more about this topic at our regular events. Together with veterinarians and animal naturopaths, we offer various face-to-face and online events .
The BICOM® bioresonance method is a cause-oriented, holistic treatment concept. It can narrow down the cause of the health problem in animals and find out even the hidden causes of the clinical picture.
Animals have a natural regulatory system that can also compensate for unusual influences. However, even good self-healing powers eventually reach their limits. Persistent exposure to allergens, environmental toxins, fungi, viruses, bacteria or stress and changed living conditions weaken the immune system and are often the cause of an illness. In particular, fungal infestation on the skin or chronic diseases in general are not always due to a breeding-related genetic defect, but are signs of a disturbed immune system.
The BICOM® bioresonance method is the key to successful diagnosis and therapy, especially for animals that cannot tell us exactly where it hurts or what the symptoms are. It is a gentle form of therapy that can be carried out without side effects and without additional stress for the animal.
The BICOM® mobile VET records the bioenergetic state of the animal, processes the information it contains and returns modified vibrations / therapy frequency patterns to the animal. Symptoms and stress can be diagnosed and targeted therapy can be initiated.
Through the use of endogenous and exogenous substances, the body’s own self-healing powers can be activated and imbalances that have existed for a long time can also be regulated.
REGUMED Medizintechnik are pioneers of the BICOM® bioresonance method. More than 30,000 therapists worldwide, well over 10,000 of them in Germany, successfully use their therapy concept.
Biophysical basics of the bioresonance method
Life is only possible when three conditions are met: matter, energy and information.
We also find these aspects in conventional medicine, both in diagnostics and in therapy. For example, every drug is also a carrier of information.
Information is neither energy nor matter, it is immaterial and comparable to the meaning of a message from a sending to a receiving system.
In addition to the electrical processes in the receptor proteins and biomembranes in general, electromagnetic interactions through light (biophotons) also play a role in cell communication and the transmission of information.
Specific electromagnetic wave patterns act as information carriers. These wave patterns can be modulated by the BICOM® device in order to eliminate disturbing or stressful information in an organism.
The goal is to restore the free flow of healing information (cell communication) and thus support the self-regulation of the organism and the self-healing powers.
Individual, patient-specific information or information from native substances, digitized substances or information stored on storage media can be used for therapy.
What your colleagues are saying…

Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Its Diagnosis
Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Its Diagnosis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a chronic autoimmune thyroid disease that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and impaired function. In this blog post, we will explore Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, its symptoms, and how it is diagnosed, including the significance of specific thyroid antibodies like Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TG-AB) and Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPO-AB). Understanding this disease is crucial for individuals experiencing hypothyroidism symptoms or chronic thyroid inflammation. Let’s delve into the details.
What is Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, also known as Hashimoto’s disease, is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland. This results in inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis), which leads to a decrease in the thyroid gland’s ability to produce thyroid hormones, causing hypothyroidism. As the disease progresses, the thyroid may become enlarged, a condition known as a goiter.
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and other essential bodily functions by releasing thyroid hormones. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the body produces antibodies that target the thyroid tissue, resulting in chronic thyroid inflammation and eventually leading to thyroid hormone deficiency.
Symptoms of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
The symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are often subtle and can develop over time. Many individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis may not immediately notice any symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the disease progresses and thyroid hormone levels decrease, the following hypothyroidism symptoms may occur:
Common Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired and lacking energy.
Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
Cold Sensitivity: Feeling cold even when the temperature is warm for others.
Constipation: Experiencing frequent constipation.
Dry Skin and Hair: Skin may become dry, and hair may thin or fall out.
Depression: Feeling down or experiencing mood changes.
Memory Issues: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
Muscle Weakness: Reduced strength, especially in the legs and arms.
Since these symptoms are also common with other health conditions, it is essential to get a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
Causes of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
While the exact cause of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is still not entirely understood, several factors may contribute to its development, including:
Genetics: A family history of thyroid disease or autoimmune disorders increases the risk of developing Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Gender: Women are more likely to develop Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, especially during or after pregnancy or in the menopausal period.
Age: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can develop at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in middle-aged women.
Environmental Triggers: Infections, excessive iodine intake, and certain medications can trigger autoimmune responses that may lead to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Diagnosing Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Proper diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis involves a combination of physical exams, medical history assessment, and laboratory tests. One of the most common diagnostic methods is blood testing, which can measure the presence of specific antibodies associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Key Tests for Diagnosing Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis:
Thyroid Function Tests: These include measuring levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) to determine how well the thyroid is functioning. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, TSH levels are usually elevated, while T3 and T4 levels may be low, indicating hypothyroidism.
Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TG-AB): This test measures the presence of antibodies against thyroglobulin, a protein produced by the thyroid gland. High levels of TG-AB suggest an autoimmune attack on the thyroid and are commonly seen in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPO-AB): This is another blood test that measures antibodies against thyroid peroxidase, an enzyme essential for thyroid hormone production. Elevated TPO-AB levels are a hallmark of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and indicate ongoing inflammation of the thyroid.
Additional Diagnostic Procedures:
Ultrasound of the Thyroid: A thyroid ultrasound may be used to check for any enlargement or abnormal growths in the thyroid gland.
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy: In some cases, if the thyroid shows signs of nodules, a biopsy may be recommended to rule out thyroid cancer.
Early Diagnosis and Monitoring
Since Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can develop gradually, it’s crucial for individuals experiencing unexplained symptoms of hypothyroidism to seek timely diagnosis and treatment. Regular monitoring through blood tests and thyroid ultrasounds can help track the progression of the disease and adjust treatment accordingly.
Treatment Options for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
While there is no cure for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the condition can be managed effectively with appropriate medical intervention. The primary treatment for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis involves hormone replacement therapy to normalize thyroid hormone levels and alleviate hypothyroidism symptoms.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
The most common medication for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is levothyroxine, a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). This medication helps to restore normal thyroid hormone levels and relieve symptoms of hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage of levothyroxine based on individual needs and regular monitoring of thyroid function.
Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medication, individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can benefit from making certain dietary and lifestyle changes to support thyroid health, such as:
Adequate Iodine Intake: Ensuring the diet includes sufficient iodine, which is essential for thyroid hormone production.
Anti-inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to reduce inflammation and support immune function.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help manage symptoms like fatigue and weight gain.
Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can support overall health and reduce thyroid stress.
Conclusion
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a complex autoimmune thyroid disease that can lead to hypothyroidism if left untreated. With early diagnosis, effective management, and proper lifestyle adjustments, individuals living with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. If you suspect you are experiencing hypothyroidism symptoms or have been diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
At Bioresonance Therapy, we offer personalized wellness solutions to help manage autoimmune diseases and chronic conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. For those looking to monitor their thyroid health or supplement their treatment plan, we offer specialized diagnostic kits, such as the Tableau Teeth Kit, designed to assist in comprehensive health assessments.
Take charge of your thyroid health today and explore our services to find the support you need on your wellness journey.
Treatment Priorities
For gentle and optimal treatment of the causes of diseases in animals
The BICOM® bioresonance method is predestined for use with large and farm animals such as horses , but also with dogs , cats and small animals. The treatment focus of the BICOM® mobile VET is wide-ranging. It is now used for many indications.
It recognises health deficits at an early stage and is used, among other things, for the following symptoms:
sweet itch
Feed intolerances
allergies and related diseases
COB/COPD
leishmaniasis
Lyme disease
anaplasmosis
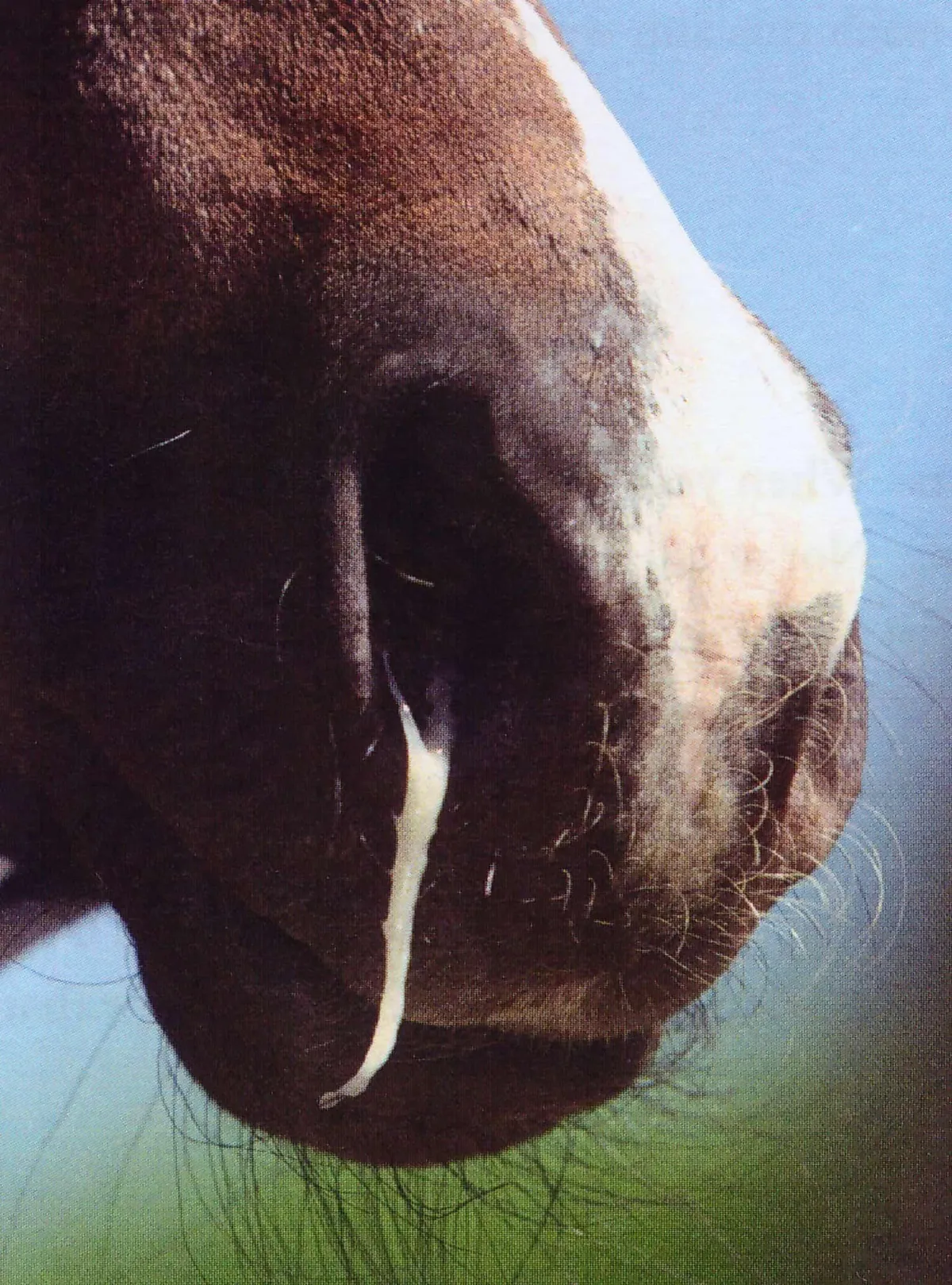
lameness in horses
hoof ulcer
Poisoning by poisoned baits, plants etc.
mauke
Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)
Cat flu/cat disease
eye/conjunctivitis
and much more
Get advice now!
Our experts are happy to be there for you personally
Our BICOM® bioresonance experts are available to answer any questions you may have
and will be happy to advise you personally and individually.



Request more information
Quick Links





Facebook
Instagram
Mail